A dynamic and powerful leadership approach, authoritative leadership style is essential in forming teams and organizations. The hallmark of this leadership style is the leader's strong feeling of control and authority, which enables them to give direction and make choices with conviction.
Possessing a strong vision, authoritative leaders persuade their followers to follow with fervor and dedication. Although there are many different types of leadership, authoritative leadership style has certain advantages that leaders and organizations must recognize in order to effectively use it.

Types of Leadership Models
The idea of leadership is complex and encompasses a wide variety of techniques and methods, each specifically designed to address unique circumstances and organizational dynamics.
Comprehending the many styles of leadership is imperative for prospective and experienced leaders alike, as it enables them to adjust and utilize the most efficient tactics to accomplish their objectives. The choice of leadership style can have a big impact on team dynamics, productivity, and overall success.
Authoritarian Leadership
A strong degree of control and power entrusted to the leader characterizes authoritarian leadership, sometimes referred to as autocratic leadership. This leadership style involves the leader making choices solely by themselves and expecting followers to do as they are told, with little to no involvement or input.
An authoritarian leader usually has a distinct vision and gives their staff detailed directives, regulations, and guidelines. When prompt and decisive action is needed, like in emergency circumstances or highly organized workplaces, this strategy may work well and they can turn into successful leaders. It can support the upkeep of order and guarantee that activities are carried out precisely.
However because authoritarian leadership tends to restrict team members' autonomy and ability to make independent decisions, it can also have negative effects including lower employee morale, decreased innovation, and decreased cooperation. The environment and particular requirements of the company or circumstance are typically critical factors in the effective implementation of authoritarian leadership.

Transformational Leadership
Beyond typical management, transformational leadership inspires and motivates subordinates to realize their greatest potential and produce extraordinary outcomes. In addition to setting high moral and ethical standards and inspiring their team with a captivating future vision, transformational leaders lead by example.
Their emphasis lies in providing personalized attention, guidance, and assistance to enable every member of the team to flourish. These leaders also promote a culture of innovation by questioning the status quo and stimulating intellectual curiosity and innovative thinking.
Transformational leadership is an effective strategy for fostering long-term success and driving change since it frequently results in more employee engagement, better performance, and a favorable corporate culture.
Transactional Leadership
A key component of transactional leadership is its emphasis on task-oriented, organized interactions between leaders and their followers. In order to manage and inspire their teams, leaders that use this strategy place a strong emphasis on well-defined guidelines, awards, and penalties.
In a transactional leadership style, team members are expected to satisfy expectations in order to be rewarded or to avoid penalties. Leaders define clear objectives and offer explicit instructions for reaching them. This approach works effectively in companies with well-established procedures and routines because it keeps things organized and guarantees that jobs are done quickly.
However it could not be as successful in encouraging innovation or team members' personal development as transformational leadership, and it might not have the inspiring and long-term vision components.
Ethical Leadership
A principled approach to leadership, ethical leadership strongly emphasizes moral principles, integrity, and ethical behavior. In addition to modeling moral behavior for their teams, ethical leaders also encourage and mentor others in acting morally and responsibly toward society.
They ensure that their activities are in line with moral principles and the organization's values by making decisions that are transparent, equitable, and accountable. A culture of trust, respect, and corporate social responsibility is fostered by ethical leadership, and it frequently results in higher employee engagement, a better-known company, and long-term success.
Being an ethical leader means setting an example for others to follow and creating a culture that values and encourages moral decision-making.
Coercive Leadership
When a leader employs coercive leadership, they mostly utilize power, intimidation, and punishment to sway and manage their followers. When a leader uses a forceful style, they assign duties, make decisions all by themselves, and demand that their team members comply right away.
This approach can work well for crisis management or other circumstances requiring quick, decisive response. But it frequently has serious disadvantages. Coercive leadership can result in a bad working atmosphere, low morale, and a lack of invention and originality among team members.
In general, it is not the best option for scenarios that call for team members to work together and take the initiative. In contemporary leadership theories, participatory and empowering leadership styles that foster employee engagement and motivation are frequently regarded as more desirable than coercive leadership.
Rather than relying too much on coercive techniques, effective leaders usually select their leadership style based on the particular demands and dynamics of the circumstance.
Benevolent Leadership
Benevolent leadership, often referred to as benevolent autocracy, is a type of leadership in which a leader maintains authority over their subordinates while showing them compassion and nurturing. With this strategy, team members' well-being is prioritized while decision-making is done on behalf of the team by the leaders, who assume a strong guiding role. To foster a healthy and encouraging work atmosphere, benevolent leaders frequently provide their team members with safety, guidance, and support.
This type of leadership may work well in circumstances requiring prompt decision-making, unambiguous direction, and personnel needing direction and assurance. However, because decision-making power is centralized, it might not be as effective in encouraging freedom and innovation among team members.
The concept of benevolent leadership is frequently linked to a paternalistic leadership behaviors in which the leader takes on a caring and protecting role. Leaders who use this approach must strike a balance between exercising authority and supporting personal development and initiative.
The nature of the duties, the preferences and demands of the team members, and the company culture all affect how successful benevolent leadership is. It should be used carefully, as with any leadership style, taking into account the objectives of the group or organization as well as the unique circumstances.
What Is The Best Leadership Style?
The greatest leadership styles are flexible and dynamic, not dogmatically following one path. Effective leaders modify their style of leadership in response to the changing needs of their teams and assignments.
Effective leadership frequently combines transformative, transactional, and servant leadership traits. While transactional leadership offers structure and responsibility, transformational leadership focuses on inspiring and motivating people, while servant leadership prioritizes supporting and empowering team members.
Another aspect of good leadership is the capacity to use democratic or autocratic style components according to the situation. In the end, the most effective leaders have a broad range of abilities, such as effective interpersonal skills, emotional intelligence, and the ability to foster strong bonds within their teams.
The key to good leadership is knowing the situation and using the right approach to optimize team performance.

The Role of Power Distance in Authoritative Leadership
A rigorous examination of how organizational and cultural elements influence leadership dynamics is to comprehend the significance of power distance in authoritative leadership. In social psychology, the term "power distance" describes how much members of a community tolerate and anticipate an unequal allocation of power.
It is clear from studying authoritarian leadership behaviors—which are defined by a leader's high level of control and authority—that power distance is crucial in determining how a leader and follower interact.
Organizational structures and cultural norms that define the efficacy and acceptability of authoritative leadership have a significant impact on this connection. In order to help leaders and organizations successfully navigate this challenging terrain and accomplish their objectives.
Influence on Employee Outcomes
Numerous employee outcomes are significantly impacted by the authoritative leader's use of power distance. It can influence workers' job happiness, engagement, and performance in addition to how they view and react to their leaders. In authoritative theory of leadership leadership, power distance can affect employee results in the following significant ways:
Job Satisfaction: Employees may tolerate—even expect—a more authoritarian leadership style in companies with a high power distance culture. If the leader's authoritative style fits with the cultural norms, this might result in increased work satisfaction. However, a strong authoritarian style may result in poorer job satisfaction since employees may feel disempowered and devalued in cultures with lesser power distances or in companies where workers prefer more collaborative leadership.
Employee Engagement: There are several ways that power distance may affect employee engagement. Employee engagement may decrease under highly authoritarian leadership in low power distance cultures, while it may increase in high power distance cultures where employees are more receptive to authoritative leadership. Effective employee engagement frequently necessitates modifying leadership philosophies to fit the cultural setting.
Performance: There might be subtle differences in the impact of power distance on employee performance. In some circumstances, forceful leadership may inspire high performance, particularly when prompt and decisive action is required. Employee performance may suffer, though, if they feel that the boss is being domineering or oppressive. This is because they may lose interest and motivation.
Turnover: Because workers are more likely to accept and adjust to an authoritative leader's style, high power distance businesses with this type of leadership may have lesser turnover. On the other hand, if authoritative leadership is not well-received, low power distance organizations may have increased turnover as staff members look for more participatory and collaborative work cultures.
Job Stress: Because they may feel more at ease with a clear line of command and well-defined duties, individuals under authoritative leadership in a high power distance culture may experience less job stress. On the other hand, workers in low power distance cultures may feel more stressed at work since they don't feel like they have as much control or say in decisions. According to empirical studies this management style and its role of power distance may not have a positive influence over causal relationships.
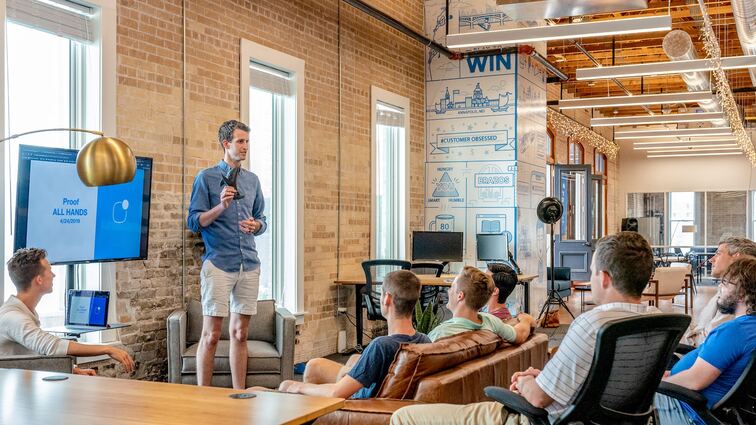

Positive Relationships & Outcomes
Good working connections have a significant influence on people's and organizations' productivity and well-being. A pleasant and peaceful work atmosphere is facilitated by individuals who get along well with their managers and coworkers. This then has a number of beneficial effects.
Positive relationships at work are the first step in improving employee morale and job satisfaction. People are more likely to be happy in their employment and find fulfillment in their work when they get respect, value, and support from their peers and superiors. This happy emotional state has the potential to be a strong motivator and improve overall work output.
Enhanced productivity is a crucial consequence of constructive working interactions. Good communication, cooperation, and teamwork are frequently the cornerstones of healthy partnerships. It is one of the positive outcomes of authoritative leadership.
Colleagues who trust and get along well with one another typically collaborate more effectively, which boosts output. Positive interactions produce a synergistic impact that facilitates the free exchange of ideas and improves task completion.
Strong bonds with leadership on employee performance also act as a protective barrier against working stress. Workers who have friends and allies at work are better able to handle stress at work. When people need it, supportive partnerships offer both practical and emotional support for their emotional intelligence, enabling them to overcome obstacles and preserve their psychological well-being.
Furthermore, a higher rate of employee retention may result from these solid relationships with superiors and coworkers. People are more inclined to stick to their existing positions when they feel appreciated and connected by their employer. Strong connections may help reduce high turnover rates, which can be expensive for businesses.
Moreover, strong bonds between coworkers raise employee engagement levels. Employees who are engaged are more devoted to their work, put up more effort, and are more willing to go above and beyond to accomplish company objectives. A strong sense of belonging and a common goal can inspire people to perform to the best of their abilities in their jobs.
Positive working connections not only provide immediate advantages but also present chances for both professional and personal development. Employees may grow professionally, acquire insightful knowledge, and enhance their skill set by receiving mentoring and coaching from peers or superiors. These relationships provide a positive learning atmosphere that is advantageous to each employee as well as the company overall.
Positive interactions also have a wider cultural impact throughout the firm. Top talent may be attracted and retained in an open and inviting work environment that appreciates and fosters these relationships. Long-term success and a better reputation can result from an effective company culture built on solid connections.
Finally, these connections can improve work-life harmony. Effective management of personal and professional life is facilitated for employees by empathetic and accommodating colleagues and superiors. Thus, a better work-life balance and increased job satisfaction may result.
Negative Influence & Outcomes
Bad working connections may have a negative impact on people and companies, which can result in a number of unfavorable consequences. A hostile and unproductive work environment can result from strained or poisonous interactions between coworkers and between staff members and managers. These interactions may have a detrimental impact on employees' well-being and the performance of the firm in a number of ways.
Decreased job satisfaction and morale are among the most obvious and immediate negative effects. People who operate in environments where there are unfavorable relationships frequently feel stressed, frustrated, and disconnected. Previous studies show that role of power distance destroy the positive relationships between a non-transactional leader and employees which create negative effects on employees.
This can thus result in a decline in job satisfaction and general discontent with their positions. Employee disengagement lowers the likelihood that they will put in their best effort, which can have an impact on motivation and productivity.
Anxiety and stress levels might also rise as a result of toxic interactions at work. Relationships that are hostile or dysfunctional with coworkers and superiors can be emotionally draining and harmful to mental health.
These connections can cause stress, which can have a negative impact on one's health and ability to perform at work through a variety of physical and psychological symptoms. Elevated levels of stress can also be a factor in burnout, absenteeism, and turnover—all of which are expensive for businesses. The effects of authoritarianism can show the difference between individuals.
Diminished productivity and cooperation are further adverse consequences of toxic working interactions. It may be difficult for people who are involved in fights or who are in tense relationships to work well together or to be honest with their coworkers.
This might make it more difficult for workers to finish projects and meet company objectives as they could be less inclined to collaborate effectively, exchange ideas, or offer assistance.
These connections have a detrimental effect on staff retention as well. If there are persistently bad interactions at work, employees may look for other jobs to avoid the negative consequences of such connections. Organizations that have high turnover rates may have financial and operational difficulties as a result of the expense of hiring new employees, providing training, and losing productivity.
Study variables show that these connections may also be detrimental to an organization's reputation. A bad work culture may spread extensively, harming the company's reputation and making it challenging to draw in top people. Internal problems can also be discovered by clients, customers, and business partners, which might damage credibility and confidence.

The Impact of an Authoritative Leader on Organizational Goals and Employee Performance
Unquestionably, leadership plays a crucial role in organizations, and the effects of various leadership philosophies on both the objectives of the latter and worker productivity are issues of lasting importance. Among these approaches, authoritative leadership is one that sticks out as unique and frequently effective. The effects of authoritarianism has notable contributions to the role of subordinates.
Decisiveness, vision clarity, and a strong sense of control are qualities that define authoritative leaders and enable them to effect change and produce desired outcomes. This function of leadership is essential for determining how a company will develop as well as how well-motivated its workforce will be.
Benefits of an Authoritative Approach to Leadership
There are several advantages to an authoritative style of leadership, particularly when applied to certain circumstances and organizational objectives. The following are some benefits of employing assertive leadership:
Quick Decision-Making: Authoritative leaders are renowned for their capacity for making choices quickly and decisively. This leadership style makes sure that actions are executed quickly in times when time is of the utmost, as during crises or important business decisions, reducing delays and any bad effects.
Clear Direction: Authoritative leaders provide their teams a distinct and unmistakable vision and direction. Employee understanding of roles and duties is aided by this clarity, which also helps to promote alignment with company objectives and lessens misunderstanding.
Accountability: Authoritative leadership encourages responsibility by setting clear standards and establishing a well-organized chain of command. Because everyone in the team is aware of their responsibilities, measuring and evaluating both team and individual performance is made simpler.
Crisis Management: Crisis management is a skill that authoritative leaders are excellent at. In turbulent times, they can keep things under control and offer a feeling of stability, which is crucial for guiding an organization and reducing disturbance.
Efficiency and Productivity: By getting rid of pointless procedures or other barriers that impede work, an authoritative leadership style can increase productivity. Following instructions can cut down on time spent on discussion and boost productivity among team members.
Open Lines of Communication: Teams under the direction of authoritative leaders usually have open lines of communication. They make sure that staff members are informed by clearly outlining their goals, expectations, and the reasoning behind their choices.
Structured Learning: An authoritative leader may make sure that staff members follow rules or protocols in businesses that have them. This can be especially helpful in sectors of the economy where safety and compliance regulations are stringent.
Change Management: Prominent leadership can successfully steer an organization's implementation of major changes or restructuring. A smoother transition can be facilitated by the leader's strong vision and capacity for change management.
Predictability and Consistency: The authoritative style encourages leadership that is predictable and consistent, which can help to establish a stable work environment. For workers, this consistency may be comforting and lessen uncertainty.
Clarity of Purpose: Authoritative leaders are capable of inspiring a feeling of purpose in their teams by sharing a compelling vision. This may result in heightened drive and a strong dedication to reaching common objectives.
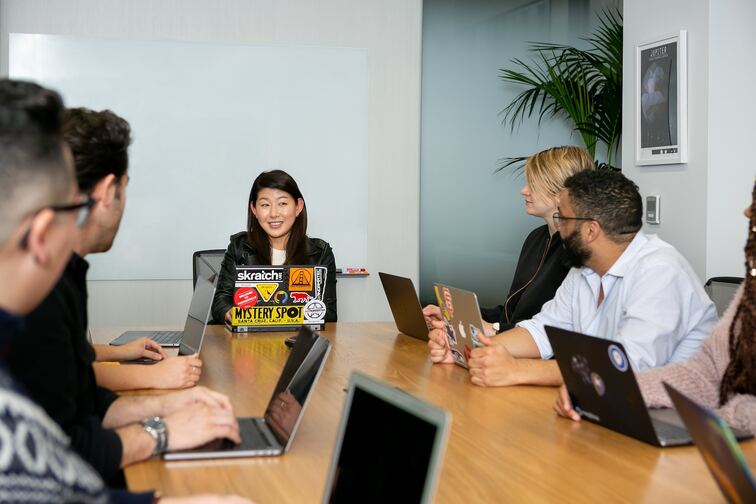

Potential Drawbacks to an Authoritative Style of Leadership
While there are times when an authoritative leadership style is advantageous, there are also possible disadvantages. One of the main issues is that, because it frequently provides little room for team member participation and ideas, it can discourage creativity and innovation within a team.
Furthermore, when employees' opinions are ignored during decision-making, they may feel devalued or disempowered, which can lower their morale and job satisfaction. Additionally, this management approach may foster a top-down, hierarchical company culture that stifles candid discussion and prevents employees from advancing to leadership positions.
Over-reliance on authoritative leadership can eventually lead to a workforce that is less engaged, motivated, and flexible. As a result, it is less appropriate for dynamic, creative work environments where creativity and collaborative problem-solving are critical.
In order to maintain a productive, engaged, and empowered team, effective leaders understand the necessity of striking a balance between forceful leadership and alternative approaches.
Individual Differences and the Effectiveness of an Authoritative Leader
An authoritative leader's efficacy can be greatly impacted by the individual variances among team members. Employee reactions to forceful leadership can be influenced by a variety of factors, including personality, communication preferences, and cultural background.
Certain individuals could flourish in a regimented and prescriptive setting, valuing the leader's lucidity and determination. Some, on the other hand, could find this approach oppressive and demoralizing, especially if they respect independence, innovation, and group decision-making.
Knowing how each person is unique, a competent, authoritative leader adjusts their style accordingly, giving opportunities for input and feedback and being more flexible as needed to suit a range of preferences.
A more inclusive and encouraging work atmosphere may be fostered by authoritative leaders who take into account and value each team member's individual needs and qualities.
Be The Leader You Want To Be
BeforeSunset AI Teams makes leading a team easier than ever. See what your team is doing and how they are feeling from a single software. Try it out today for free!