FTE is an abbreviation for full-time equivalent, which is a measure of a company's number of full-time employees based on the hours worked by part-time employees. You may be thinking how will FTE benefit me?
FTE calculation is beneficial to your business because it is used to establish the number of full-time employees a company employs, even if the employees work part-time or on a contract basis. This is critical for organizations to understand since it affects workforce requirements, budgeting, and compliance with labor laws.
In this blog, we will show you what FTE is and explain how it is calculated, also how to calculate FTE for a business that is only open for a few months of the year.
How to Calculate Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)?
If your employees put in 40 hours a week, it means they are employed full-time. 2,080 hours are worked by a full-time employee who works 52 weeks a year. The annual working hours of your workforce can be added up and divided by 2,080 to determine FTE.
Consider that you have 17 employees that put in a combined 20,800 hours a year. This is equivalent to 10 FTEs. The same method can be used to create FTEs for a certain month, quarter, or even a single day.
Of course, not every full-time employee works for 40 hours a week and 52 weeks a year because of sick leaves, vacations, holidays and time-offs. You can add these to consideration while calculating EFTs.
Let's go step by step.

1st step: Make a list of your employees and their working hours.
You can create a board, chart, table or graph. Whatever you are comfortable with!
2nd step: Write down which schedules they are on.
Full-time or part-time.
3rd step: Calculate the hours according to your need.
You can calculate the hours worked per year or week. It is up to your need.
If you want to calculate the hours worked per year, you should multiply the hours by the weeks in a year, which is 52.
4th step: Calculate part-time FTE with easy calculation.
You just have to divide the total part-time working hours by the total full-time hours. Because with FTE, your determinant in the equation is the total full-time working hours.
5th step: Determine the total FTE
Add the number of full-time workers to the part-time FTE you just calculated.
That's it! Now you have the total FTE.
If you want an easier example of how to calculate FTE, don't worry, we are here for you.
It is really easy to calculate FTE and we will demonstrate it with simple numbers and examples!
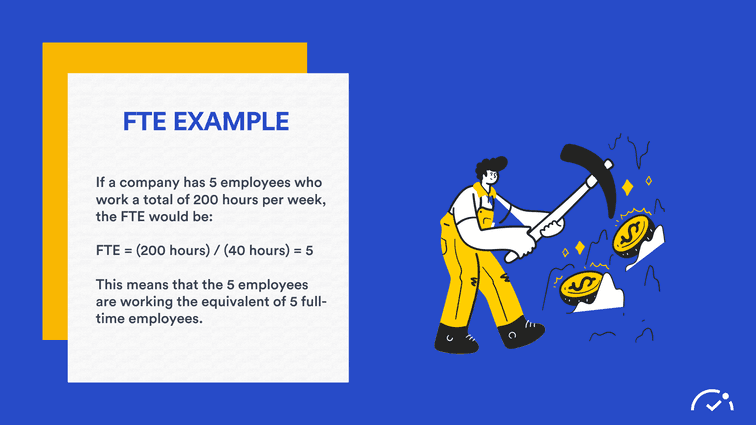
Here is an easy example of how to calculate FTE:
Let's say full-time working hours for a week is 40 hours;
If one employee is working for 40 hours,
one works for 35 hours,
one works for 20 hours,
and another works for 10 hours.
To calculate FTE, you should add those together and divide them by the full-time working hours;
40+35+20+10= 105 hours of total working time per week,
105/40= 2,625 FTE
In other words, it is calculated that it corresponds to 2,625 full-time employees.
What factors should you consider when calculating FTE?
When you are calculating full-time equivalent (FTE) employees, you should look at how many hours each person works and how many people work in a certain role or department.
Other things that might be taken into account are how many vacation days or paid time off employees take, as well as any other types of leave that might change the number of hours worked. You should also think about how many part-time workers you have and how many hours they work.
How Do Businesses Use FTEs?
Businesses use FTE (full-time equivalent) as a measure of the size of their workforce. If you are wondering why is that because it can serve several purposes that will benefit them such as:
Budgeting and forecasting: Full-time equivalents (FTEs) is often used to estimate the number of personnel and associated costs needed to satisfy company objectives such as revenue targets or output quotas.
Another way FTEs can be used is to distribute resources such as office space, equipment, and supplies among different departments and teams.
Compliance: It can be used to assure compliance with laws and regulations pertaining to workforce sizes, benefits, taxes, and safety can be examples of this.
Staffing: FTEs can be used to calculate the number of employees needed to meet demand and to prepare for future recruiting and layoffs.
FTEs can be used to quantify staff productivity and efficiency by comparing the number of FTEs to variables such as revenue, output, or customer satisfaction.
Human Resources: Full-time equivalents (FTEs) are also used in human resource management to prepare for employee benefits, remuneration, and other HR-related costs.
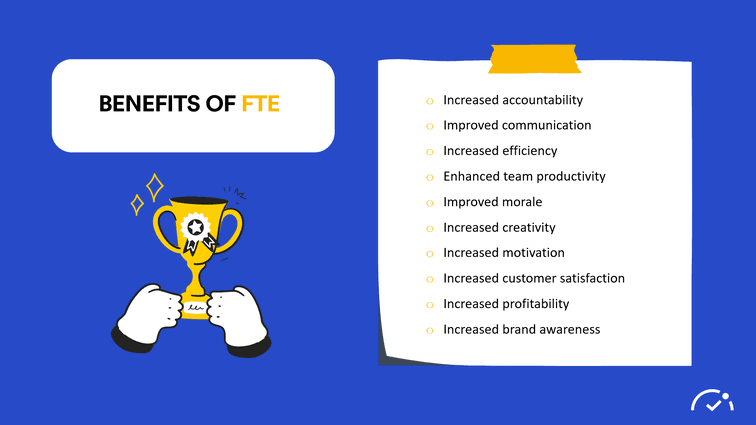
The Benefits of Using FTE?
When you use FTEs, it's simple to measure how well you're doing at work, especially if you have part-time employees. You can contrast your staffing level with your competitors in your industry after converting part-time meters to FTEs. Additionally, FTE can benefit you in terms of making your work effort easier while calculating income, productivity, and profit per employee.
1. Increased accountability
Increased accountability means being able to measure and keep track of how productive and efficient employees are. By figuring out FTE, an organization can get a better idea of how many employees it needs to do a certain job and see where it may be overstaffed or understaffed.
2. Improved communication
The ability to better coordinate and communicate with employees, as well as among different departments or teams within an organization is called improved communication.
3. Increased efficiency
An organization can make the best use of its resources and workers by calculating FTE which will result in an increase in efficiency. Also, it can help find places where work isn't being done as efficiently as it could be. This can be fixed through process improvements or training.
4. Enhanced team productivity
FTE is used to figure out how productive a team or organization is by dividing the number of full-time employees by the total number of hours worked by all employees. Adding more FTEs to a team or organization can make them more productive. This can be done by hiring more people, giving current employees more hours to work, or putting in place better processes and technologies.
Improved efficiency – FTE allows you to accurately assess the amount of resources needed for a project and scale up or down as the project progresses.
Streamlined workflow – FTE allows teams to be more organized and efficient with their work, resulting in less time spent on managing resources and more time focused on getting the job done.
Reduced cost – With FTE, you can ensure that you are assigning the right amount of resources and not wasting time and money on over-hiring.

5. Improved morale
Employee morale might improve if the number of FTEs hired increases. Staffing levels can have a significant impact on workers' happiness and health because fewer hours spent working and fewer worries about getting everything done may result. Staff expansion has the potential to improve teamwork and morale by making it simpler for employees to work together.
6. Increased creativity
There could be a link between the number of full-time employees in a firm or organization and the number of new ideas they generate. More people can contribute their unique thoughts and perspectives to assist solve problems and make key decisions when you have a larger team.
The workplace can become more creative and productive when more individuals collaborate, share ideas, and build on one another's work. Even though increasing the number of full-time equivalents (FTE) may result in more creative work, it is crucial to realize that creativity has many different components and is influenced by a variety of factors.
7. Increased motivation
Increased employee morale typically translates into increased productivity and performance, allowing a larger number of employees to complete the same amount of work with fewer FTEs. FTE is a commonly used statistic for determining staffing requirements and workloads, as it indicates the total number of hours worked by an individual or team.
As a rule of thumb, the equivalent number of part-time workers is derived by dividing the total number of working hours by the number of hours worked by a full-time employee. So we can say that FTE is good for morale and your employees will work even better with FTE.
8. Increased customer satisfaction
More pleased customers can give a firm a variety of benefits, including better income, repetition of business, and favorable word of mouth. This may boost demand for goods and services, increasing the number of full-time equivalent (FTE) workers required to meet that demand.
Customers who are happy with the services they receive are less likely to shop, and they are more likely to recommend the company to others and return for future purchases. More money and growth equals more opportunity to hire new employees.
As an added bonus, a company with a high number of satisfied customers is more likely to have a great reputation, which could lead to increased sales and the hiring of outstanding workers. As a result of increased demand for goods and services, a larger workforce may be required.
9. Increased profitability
When your company's profitability rises, it means it's making more income. The term "full-time equivalent," or FTE, refers to the number of part-time employees who provide a company with the equivalent of full-time hours. There are several methods for raising FTE and improving profitability, such as increasing revenue, lowering expenses, and increasing productivity.
Keep in mind, however, that the specific strategies that may be most useful are depending on the organization and the industry.
10. Increased brand awareness
Increased brand awareness means that consumers are more familiar with and identify a brand. Most advertising and promotion campaigns excel at this. FTE (full-time equivalent) is a measure of how many full-time employees a company has or how many part-time employees work the same amount of hours as a full-time employee.
Increasing FTE and brand recognition can be accomplished in a variety of ways, including:
Online marketing campaigns (e.g. social media, email marketing, search engine advertising)
Traditional marketing campaigns (e.g. television, print, radio)
Public relations (e.g. press releases, events, sponsorships)
Influencer marketing
Building a strong company culture that attracts and retains employees.
But of course this can change from brand to brand, therefore it doesn't mean that every tactic will be beneficial for you.
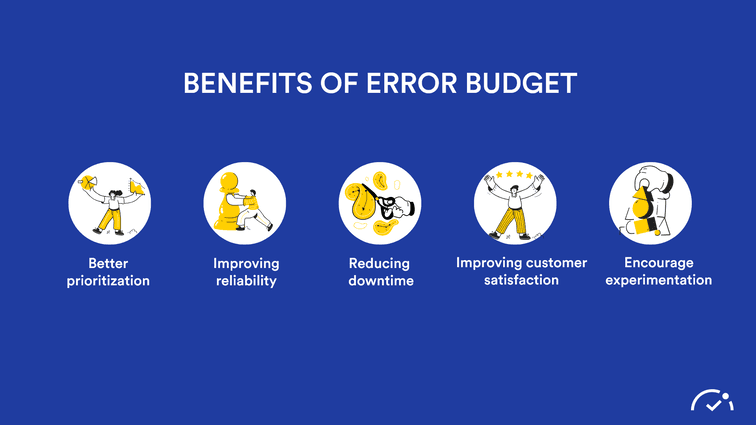
Error Budgeting: A Better Product through Embracing Imperfection
An error budget is a tool used in product development and engineering to monitor and mitigate risks associated with software and system failures. It enables teams to develop a tolerance for failure and plan for how to deal with it when it occurs.
A product can benefit from an error budget by:
Setting an error budget allows teams to prioritize items that are more vital to the product's success and ensuring that they are produced with a greater level of reliability.
Improving reliability: By setting an error budget, teams may focus on discovering and correcting the core causes of failures, thereby improving the product's overall reliability.
Reducing downtime: Teams may limit the impact of failures on customers and reduce downtime by planning for them and having a strategy in place to handle them.
Improving customer satisfaction: Teams can assist guarantee that customers have a great experience with the product by managing and minimizing risks related with software and system failures.
Encourage experimentation: By establishing an error budget, teams can feel more at ease experimenting with new features and technologies without fear of jeopardizing the product's reliability.
It is crucial to remember that error budgeting is not a stand-alone activity and should be utilized in concert with other best practices and approaches in reliability engineering.
Seasonal Workers and FTE Calculation
When determining FTE (full-time equivalent) for a business that employs seasonal workers, the number of hours worked by those employees during the season, as well as the number of weeks they are employed, must be considered.
FTE for seasonal workers can be calculated by taking the total number of hours worked by all seasonal employees during the season and dividing it by the number of hours per week that comprises a full-time position.
To give an example to that, if a company hires 20 seasonal workers for 12 weeks and each works 40 hours per week, the total number of hours worked by the seasonal workers is:
20 employees times 12 weeks times 40 hours per week is 9,600 hours.
To calculate the FTE, divide the figure by the number of hours per week required for a full-time position (40 hours per week).
9600 hours divided by 40 hours per week equals 240 FTE.
Another method you can try is to take the number of hours worked by the seasonal worker and divide it by the number of hours per week that comprise a full-time position, then multiply that figure by the number of weeks worked, and you will get the FTE for that worker.
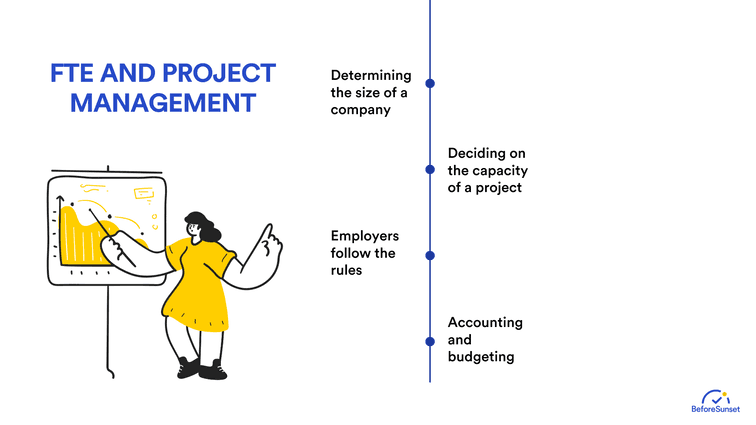
FTE For Project Management
FTE offers a systematic method to determine the requirement for upcoming projects and the number of hours needed to complete tasks. As a result, it is a very beneficial measurement tool for long-term business strategy. You can determine how many hours your project needs, and after calculating the equivalent EFT of that hour, you can hire the number of people the project requires to be completed. In addition, you can hire part-time workers for short-term projects.
Determining the size of a company
Because FTE includes both full-time and part-time employees in the equation, you will be able to know the number of hours worked in the company rather than the employees. The twist here is that you will know the hours worked in your company by its equivalent to full-time workers!
Deciding on the capacity of a project
With FTE, you can hire full-timers and part-timers for the same project. This way, you can be able to have the average number of employees needed for a project to be done rather than overstaffing. Each employee can have a specific role, therefore, it would be easier for everyone to focus on their work without experiencing miscommunications, and each employee can contribute to the project knowing their exact role in the project.
Employers follow the rules
FTE can show employers when it is time to provide their employees with health insurance, and bonuses because they get timely information to keep in compliance with the law. Employers can determine whether to offer these to their employees when it is reached to a certain number of FTE.
Accounting and budgeting
This measurement tool (FTE) is really essential and critical when it comes to calculating and deciding on wages, also the costs of these payments when the wages are given to the employees.
It could be more beneficial in terms of finance when it comes to paying new part-timer employees for a project rather than overpaying already existing full-time workers. EFT can help a company discover these kinds of budget-friendly solutions.
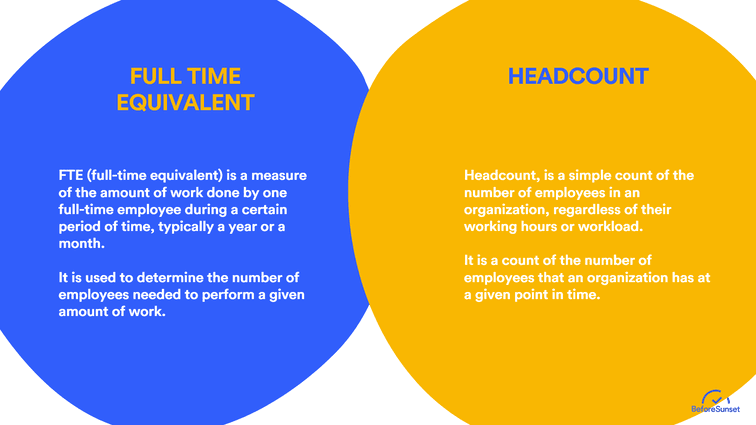
What is the difference between FTE and headcount?
To calculate an FTE (full-time equivalent) wage, take the employee's annual salary and divide it by the number of working hours per year.
Here's how to compute an FTE salary for a $50,000-per-year employee who works 40 hours per week:
Determine the number of working weeks in a year. This is usually roughly 52 weeks every year, however it might vary depending on the company's vacation policies and other considerations.
Determine the amount of working hours each year. This can be estimated by multiplying the number of working weeks per year by the number of working hours per week.
52 weeks x 40 hours per week = 2,080 hours per year
Divide the annual salary by the number of working hours per year to determine the FTE salary.
$50,000 / 2,080 hours per year = $24/hour
In this example, a person earning $50,000 per year and working 40 hours per week would have an FTE wage of $24 per hour.
It is crucial to note that this method of computation assumes that the employee works 40 hours per week, 52 weeks per year; if the employee has any paid time off, holidays, etc., the calculation may differ.
It is also worth noting that FTE salary computation is only one method of computing an employee's wage and may not be the most accurate method of establishing the employee's remuneration, especially for salaried staff; other considerations such as benefits and bonuses should also be considered.
What is %100 FTE mean?
A full-time employee who works the regular number of hours per week for their organization or industry is referred to as a 100% FTE (full-time equivalent). This is typically 40 hours per week, however it might vary based on the firm or industry. A 100% FTE is generally compared to part-time or reduced-hours employees, who are regarded less than 100% FTE.
For example, if a company has ten employees, four of whom work 40 hours per week and the other six work 20 hours per week, the company has six FTEs (4 full-time + six*0.5 part-time).
It is crucial to note that the definition of full-time employment varies by company and industry, therefore 100% FTE may not always mean the same thing across organizations.
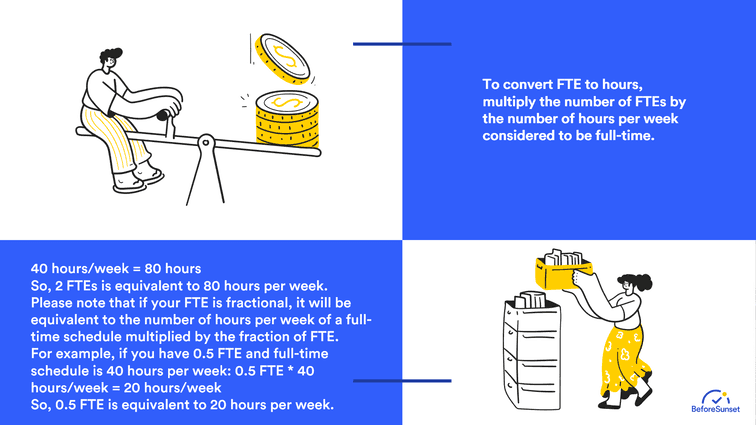
How do you convert FTE to hours?
To convert FTEs (full-time equivalents) to hours, you should multiply the number of FTEs by the number of hours per week that a full-time position requires. Of course this varies according to the company and industry, but it is usually approximately 40 hours each week.
To give and example to that, if a company has two full-time employees and a full-time workweek is 40 hours, the total number of hours worked by the two FTEs would be:
2 FTEs x 40 hours per week = 80 hours per week
It is important to remember that this computation assumes that all FTEs work full-time hours with no overtime or extra hours.
Remember that while this is the most typical method of converting FTE to hours, it might vary based on the firm and their definition of full-time.
What if you're in business for just a few months out of the year?
If you want to calculate FTE for a business that is only open for a few months of the year, you should first ascertain the total number of hours worked by all employees during the open months. Then divide that figure by the number of hours worked by a full-time employee in a year (usually 2,080). This will give you with the amount of FTEs for the company during the open months. Calculating FTE is easy If you learn the technique.
Using FTE for Productivity and Efficiency Analysis
When it comes to financial planning and enhancing operational efficiency, understanding the productivity of your workforce is essential. One effective method to achieve this is by utilizing Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) employees.
This metric provides a standardized unit of measurement that allows businesses to assess the productivity of employee types across the entire organization. Here’s how using FTE can aid in productivity and efficiency analysis:
Understanding FTE and Its Application
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) employees is a key metric that translates the hours per month and part-time hours of different employee types into a common full-time schedule. This conversion allows you to analyze productivity on a full-time basis.
Steps to Analyze Productivity and Efficiency with FTE
Collect Data on Hours Worked: Gather information on actual hours worked by individual employees, including those working part-time hours. This data should cover an annual basis to provide a comprehensive view.
Convert Hours to FTE: Calculate the full-time equivalent for each type of employee by dividing their hours weekly by the standard full-time hours. For example, if a single employee works 20 hours per week, their FTE would be 0.5.
Analyze Performance by Employee Type: Compare the FTEs of various employee types to determine which groups are contributing most effectively. This analysis helps in understanding how full-time work and part-time hours affect overall productivity.
Evaluate Client Projects and Future Projects: Use FTE data to assess the efficiency of your client projects and plan for future projects. This insight helps in optimizing resource allocation and improving the execution of client projects.
Review Historical Data: Examine the previous calendar year to identify trends and changes in productivity. Comparing these with the current year helps in understanding shifts in efficiency and planning adjustments accordingly.
Benefits of Using FTE for Productivity and Efficiency
Accurate Productivity Measurement: By using FTE, you can more accurately measure the productivity of full-time equivalent employees versus part-time hours and other employee types.
Improved Financial Planning: Understanding how different employee types contribute to productivity helps in refining your financial planning and optimizing employee salary expenditures.
Enhanced Resource Allocation: With clear insights into the productivity of various employee groups, you can allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that each single employee contributes to their maximum potential.
Strategic Decision Making: FTE analysis provides valuable data for making strategic decisions regarding hiring, project management, and overall business operations.
Optimized Business Operations: By evaluating normal course load and the efficiency of full-time work, you can streamline business processes and improve overall operational efficiency.
Example from a Sample Company
Consider a sample company with a mix of full-time and part-time staff. By calculating the FTE for each employee type, the company can determine the true contribution of each group.
For instance, if the analysis shows that part-time workers are contributing significantly to client projects but less to full-time equivalent tasks, the company can adjust its resource allocation to better align with project needs and improve productivity.
In conclusion, leveraging FTE for productivity and efficiency analysis helps businesses gain a clearer understanding of their workforce dynamics. This approach enables better financial planning, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced decision-making, ultimately driving business success and efficiency.
Optimizing Part-Time and Seasonal Workforce with FTE
In the dynamic landscape of modern businesses, optimizing the full-time and part-time employees and seasonal workforce becomes a crucial step for business owners. Calculating the Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) for these categories provides valuable insights into the actual hours worked, helping in making informed decisions and enhancing business growth.
Understanding Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is a metric that translates the hours worked by part-time employees and seasonal workers into the equivalent of a single full-time employee. This calculation is based on a standard 40-hour work week, representing the typical hours a full-time employee works.
Steps to Calculate FTE for Part-Time and Seasonal Employees
List Employees and Their Hours: Make a comprehensive list of all part-time and seasonal employees, noting their hours per month and actual hours worked.
Determine Weekly Hours: Calculate the total weekly hours worked by each employee. This step provides clarity on their full-time schedule equivalency.
Convert to Annual Hours: Multiply the weekly hours by the number of weeks they work in a year to get the annual hours. This helps in understanding the normal course load and total hours of service provided over a period of time.
Calculate FTE: Divide the annual hours by the standard hours a full-time employee works in a year (typically 2,080 hours). This gives the FTE value, representing how many full-time employees the part-time and seasonal workers equate to.
Practical Example
Assume a business has 10 part-time employees working an average of 20 hours per week for 50 weeks a year:
Total Weekly Hours: 10 employees * 20 hours = 200 hours per week
Annual Hours: 200 hours/week * 50 weeks = 10,000 hours per year
FTE Calculation: 10,000 hours / 2,080 hours = 4.8 FTE
This calculation shows that the 10 part-time employees are equivalent to 4.8 full-time employees in terms of hours worked.
Benefits of Using FTE for Workforce Management
Accurate Budget Considerations: By knowing the FTE, business owners can make better budget decisions, understanding the actual costs associated with the workforce.
Improved Business Process: Optimizing the workforce based on FTE leads to streamlined operations and more efficient business processes.
Enhanced Profitability: Understanding the profits per employee becomes easier when FTE calculations are used, providing insights into business growth and profitability.
Effective Resource Allocation: FTE helps in making informed decisions about resource allocation, ensuring that the actual workload matches the capacity of the workforce.
Strategic Planning: Business owners can plan for future growth and expansion with a clear understanding of their workforce's real performance and capacity.
Using FTE calculations for full-time and part-time employees allows business owners to gain a comprehensive view of their workforce, facilitating better management and more informed decision-making. This approach not only helps in optimizing the workforce but also in driving overall business success by aligning resources with actual needs and business goals.
The Importance of FTEs in Managing Labor Costs and Productivity
Understanding FTEs (Full-Time Equivalents) is essential for effective workforce management, particularly when calculating labor costs and scheduling. By converting hours per month and hours per week into FTEs, you can accurately assess the need for full-time work and optimize staffing. It's important for business development.
For example, if your business requires a certain number of hours per week, converting these into FTEs helps in determining how many full-time employees are needed for entire staff. This is crucial for both sole proprietorships and larger organizations. The calculation of hours into FTEs ensures you align your full-time terms with actual hours worked, making it easier to manage costs and productivity.
In essence, mastering FTEs allows you to effectively balance your full-time work needs, control labor costs, entire workforce and plan accordingly for days per week worked.
Maximizing Your Time: BeforeSunset AI
BeforeSunset AI is the perfect software for managing and keeping track of your time. Why we love it is that BeforeSunset can:
Track the time you spend on different tasks or projects: This can help you to identify which tasks take up the most time, and where you may be able to improve your time management.
By tracking the time you spend on different tasks, you can see how productive you are during different parts of the day, and make adjustments to your schedule accordingly.
We value you and your time! Why don't you try it today?


